Google releases new quantum computer chip Willow
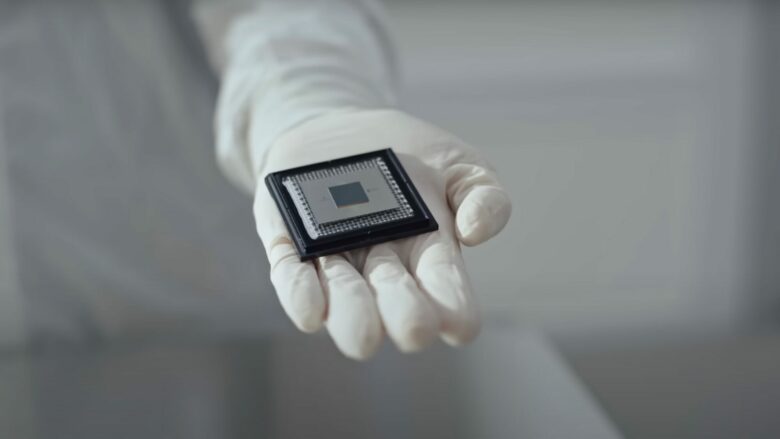

Google announced an important milestone: The self-developed state-of-the-art quantum computer chip “Willow” is said to be capable of “groundbreaking” performance. It can perform calculations in less than five minutes which would take a modern supercomputer 10 septillion. That corresponds to a number with 25 zeros which is far greater than the estimated number of stars in the Milky Way.
More Quantum Bits
The Willow chip is also said to be able to reduce errors exponentially and in real-time, as Google plans to use more qubits (quantum bits). In total, it is said to have 105 qubits, giving it the “best performance in its class.”
These are the basic units of information in quantum computing, which, unlike classical bits, represent several states simultaneously due to the quantum properties of superposition and entanglement. Classical bits can only exist in a state of 0 or 1. Qubits, however, enable quantum computers to have exponentially higher computing power than classical computers.
Improved quantum error correction
According to Hartmut Neven, head of Google Quantum AI, Google researchers have used Willow to overcome a key challenge in quantum error correction that science has been working on for nearly 30 years. Google announced back in 2019 that its quantum processor could solve a mathematical equation in three minutes, while a supercomputer would need 10,000 years to do so.
According to the IT company IBM, this claim was false. IBM, Microsoft, and Amazon are all developing their own quantum computer systems.
Quantum technology is to become “indispensable”
The quantum chip is now intended to pave the way to a large-scale quantum computer: “As part of Google Research, our team has created a long-term roadmap, and Willow takes us a long way along this path to commercially relevant applications,” says Neven.
Next, the tech giant wants to perform “useful, beyond-classical” calculations, Neven said in a blog post. By collecting AI training data, new drugs could be discovered, more efficient batteries for electric cars could be developed, and progress in nuclear fusion and new energy alternatives could be accelerated, the head of Google Quantum AI added.
The research results were published in the scientific journal Nature.